ys
ys
-
Nachrichten
-
Produkte
Produkte
Suche nach Produkten
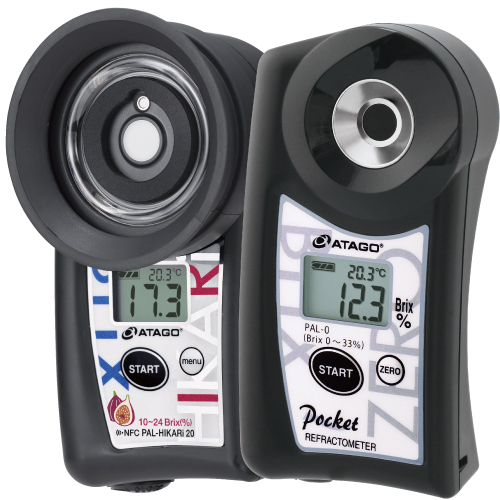
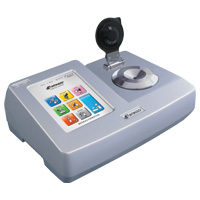
Viskosimeter pH-Messgerät Refraktometer In-Line Refraktometer IR-Brix-Messgerät Salzmessgerät ALLE ANSEHEN
Suche nach Nutzung

Suche nach Kunden
-
ATAGO Lab
-
HACCP
- Unterstützung
- Unternehmen
-

- Global