Electrical conductivity (conductivity) changes with temperature, as well as with other factors.
Even when measuring the same solution, temperatures of 15℃, 25℃, and 35℃ will give different electrical conductivity (conductivity) measurements.
As temperature rises, so does electrical conductivity (conductivity).
As temperature falls, so does electrical conductivity (conductivity).
This makes it difficult to obtain correct measurements for salt concentration using electrical conductivity (conductivity).
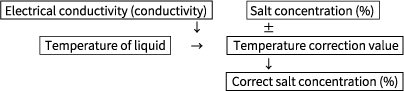
A temperature standard at 25℃ was used to create a scale that correlated electrical conductivity (conductivity) and salt concentration (%) at 25℃.
When the liquid is a temperature other than 25℃, due to the influences of salt concentration, temperature, and electrical conductivity (conductivity), the temperature correction value is determined by adjusting the correction value based on the correlation between electrical conductivity (conductivity) and salt concentration (%) at 25℃.
ATAGO ES-421 and PAL-SALT salt meters detect both the electrical conductivity (EC) and temperature of a sample and adjust the correction value based on the temperature measurement to correctly display the salt concentration (%).